Natural remedies are endorsed as an effective treatment for individuals suffering from interstitial cystitis (IC). Remedies include diet modification, nutritional supplements, herbal concoctions, or a combination of multiple therapies. Nevertheless, there are no calculable standards to predict which natural remedies will work for everyone.
In most cases, an individual will attempt a number of treatments before finding what “clicks” with their particular symptoms. Moreover, what may be effective during one flare-up may not be as effective during another; therefore, having a variety of remedies is best.
Interstitial cystitis (IC) is characterized by persistent inflammation or infection of the urinary bladder. Sometimes described as bladder pain syndrome (BPS), this chronic health issue is not limited to women. Men are just as vulnerable with similar symptoms though IC is more common in women. Because interstitial-cystitis has no cure, effective treatments are usually restricted to managing IC symptoms like severe flare-ups and swelling.
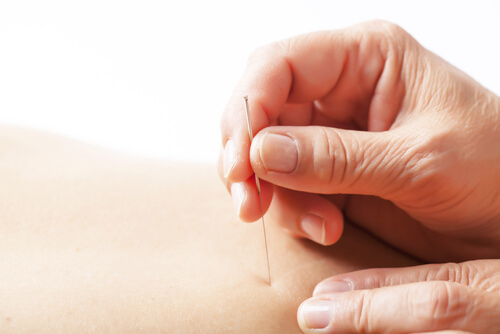
1. Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a natural method wherein specific acupoints on the body are stimulated by fine needles that penetrate the skin to relieve pain and symptoms of illness. In fact, according to the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), “acupuncture has proven to be effective against the chronic pain that many IC patients frequently suffer with.” Many IC patients affirm that acupuncture improved their condition including patients with other types of bladder infections.
The concept of acupuncture or energy medicine is based around the belief that all organisms emit a delicate energy field comparable to an aura and that nervous energy creates disease.
Bear in mind, like many therapies, acupuncture is not a “one size fits all” remedy for IC. Even so, acupuncture is an attested complementary therapy proven to educe a measured response from the hormonal, nervous, and immune system. As a result, the over-stimulation of the nerves and urinary tissues are subdued with the help of endorphins discharged from the brain.


